What is position trading and how can you apply it to your trading strategy?
Position trading is a strategy where traders hold a position for an extended period, typically ranging from several months to years.

Written by: Ioan Smith | Expert Financial Writer
What is position trading and how does it differ from other trading styles?
Unlike short-term trading strategies such as day trading or swing trading, position trading focuses on capturing substantial price movements over long timeframes by identifying and navigating major market trends.
Position trading, day trading, and swing trading each offer unique advantages and disadvantages, catering to different types of traders and investment goals. Position trading is ideal for those looking to benefit from long-term trends and who have the patience to hold investments over extended periods. It requires thorough research and a focus on fundamental analysis. Day trading suits those who thrive in a fast-paced environment and are skilled at making quick decisions based on technical analysis. It involves higher risks and stresses but can offer significant short-term returns. Swing trading strikes a balance between the two, providing opportunities to profit from intermediate price movements with less frequent trading and lower stress than day trading. It requires a good grasp of both technical and fundamental analysis to be successful.
Ultimately, the choice between these trading styles depends on individual risk tolerance, time commitment, and trading expertise.
What are the key benefits of position trading?
Position trading offers a number of key benefits:
- Reduced stress and time commitment - Position trading involves many fewer transactions compared to day or swing trading, reducing the need for constant monitoring of markets. This makes it much less stressful and more suitable for those who cannot dedicate significant time to trading.
- Lower transaction costs - Fewer trades mean lower costs and fees, which can significantly impact profitability. The reduced frequency of trades also means less sensitivity to bid-ask spreads.
- Capitalising on long-term trends - Position traders aim to profit from substantial price movements over extended periods of time. By focusing on the bigger picture, they can capture larger gains from long-term market trends rather than smaller short-term fluctuations.
- Fundamental Analysis - Position trading often emphasises fundamental analysis, including economic indicators, company financials, and industry trends. This can lead to more informed and potentially safer investment decisions.
- Tax efficiency - In many tax jurisdictions, longer holding periods can result in favourable tax treatment on capital gains, further enhancing profitability.
- Minimised impact of market noise - By focusing on longer time frames, position traders are less affected by daily market volatility and noise, which can lead to more stable investment returns.
How important is market trend analysis for position trading?
Market trend analysis is critically important for position trading, as it helps traders align investments with the broader market direction, thereby increasing the likelihood of success. By identifying and investing in leading companies in sectors within differing trends, position traders can benefit from sustained growth and expansion over the long term. This approach aligns with the fundamental principles of position trading, focusing on long-term trends and holding positions to capture potential gains as trends unfold. Long-term market trends can be split into three distinct areas - secular, cyclical and primary:
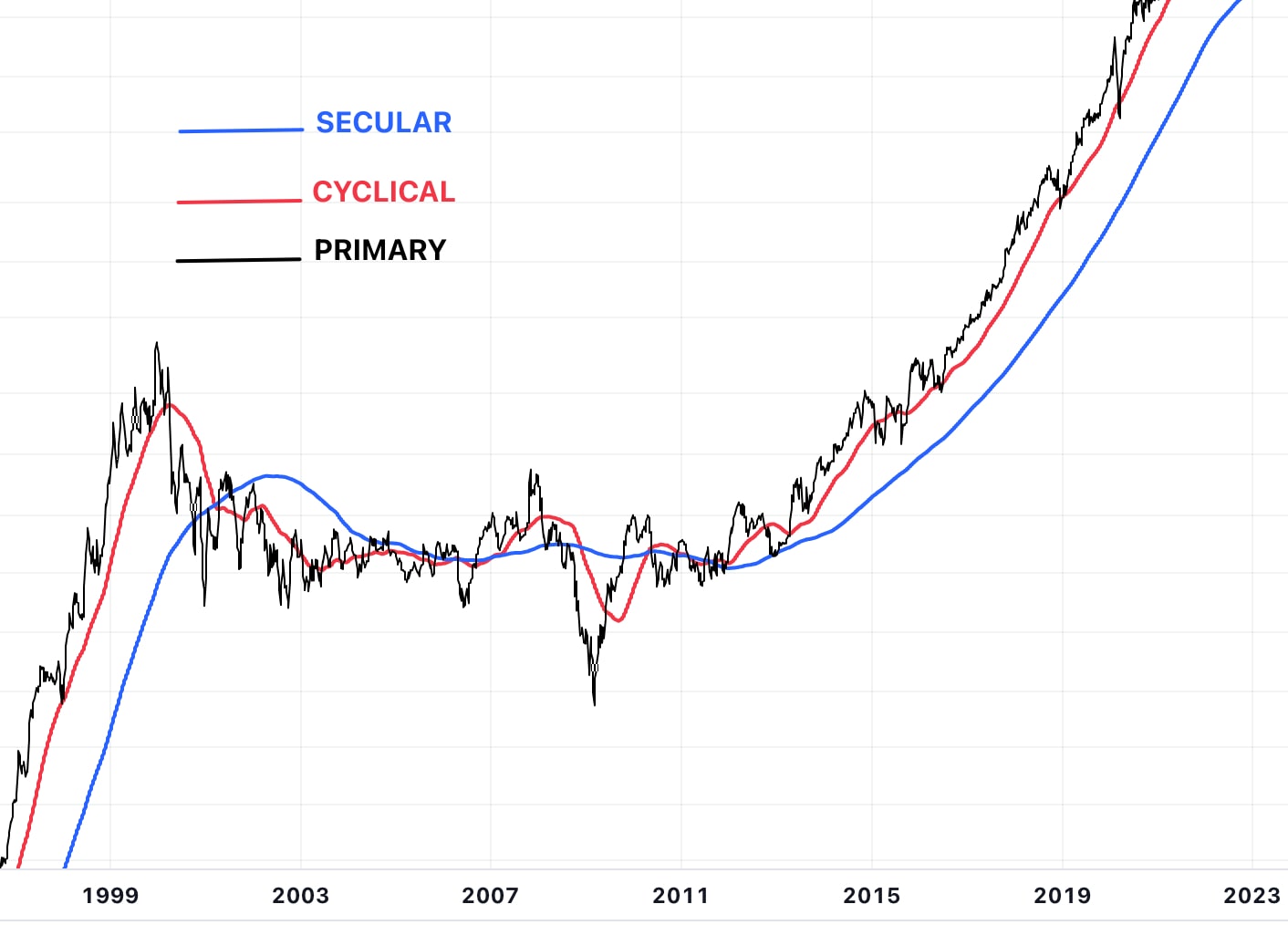
Secular trends - Long-term movements that can run several decades, often driven by broad economic changes, technological advancements or significant political shifts. Renewable energy is an example of a secular trend suitable for position trading. This long-term trend was, and continues to be, driven by several factors, including increasing environmental awareness, government policies promoting clean energy, technological advancements, and the declining costs of renewable energy production.
Investment opportunities
Position traders can continue to capitalise on this secular trend by investing in companies involved in various aspects of the renewable energy sector, such as:
- Solar Energy: Companies manufacturing solar panels, inverters, and other solar technologies.
- Wind Energy: Firms producing wind turbines and related infrastructure.
- Energy Storage: Companies developing advanced battery technologies and energy storage solutions.
Cyclical trends - Cyclical trends are medium-term market cycles that typically span from one to ten years, influenced by economic cycles of expansion and contraction. One notable example of a cyclical trend for position trading is the real estate market cycle. The real estate market typically follows a cyclical pattern influenced by various economic factors such as interest rates, economic growth, and consumer confidence.
Phases of the Real Estate cycle
By understanding the phases of the real estate cycle, position traders can strategically allocate their investments to benefit from cyclical fluctuations, thereby enhancing their long-term returns.
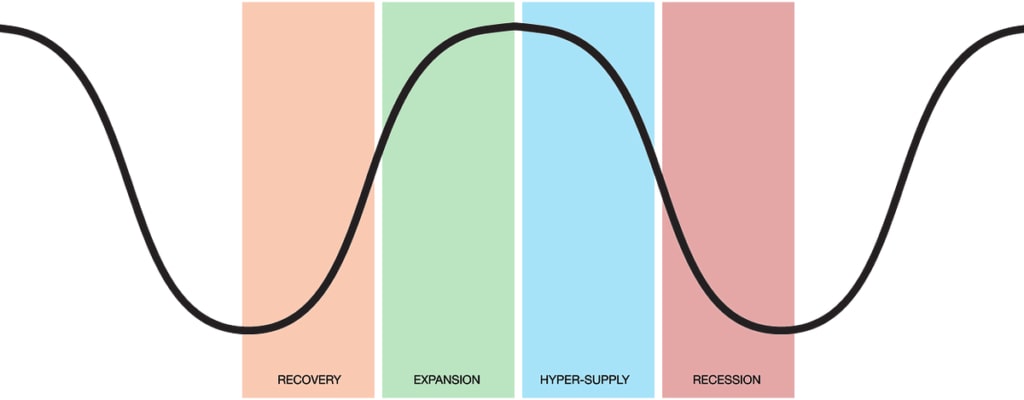
Source: https://bas-ip.com/articles/real-estate-cycle/
Recovery - The recovery represents the lowest point of the cycle, with reduced market activity and low property prices. Position traders can identify undervalued real estate stocks or REITs with strong fundamentals that are poised for recovery. Investing during this phase can provide significant returns as the market moves back into expansion.
Expansion - During the expansion phase, the economy is growing, unemployment is low, and as a result consumer confidence is high. Demand for real estate increases, leading to rising property prices and new construction projects. Position traders can capitalise on this phase by investing in real estate development companies, construction firms, and real estate investment trusts (REITs).
Hyper-supply (Peak) - The peak phase is characterised by the top in property prices and frantic market activity. The market becomes saturated with new properties and construction slows down. Position traders might consider reducing exposure to real estate stocks during this phase or taking profits from earlier investments.
Recession (Contraction) - In the contraction phase, economic growth slows, interest rates might rise, and consumer confidence wanes. Property prices begin to decline, and there is an excess supply of real estate. Position traders can look for opportunities in distressed assets or companies that may benefit from a downturn, such as those involved in property management or renovation.
Investment opportunities
Position traders can position for cyclical trends in the real estate market by:
- Timing investments: Entering the market during the expansion or trough phases to maximise gains.
- Diversifying across sectors: Investing in residential, commercial, and industrial real estate sectors to spread risk.
- Analysing economic indicators: Monitoring interest rates, GDP growth, and housing starts to predict market movements.
Primary trends: The main direction in which a market or security is moving over a long period, either upward (bull market) or downward (bear market). A primary trend that has significantly impacted the market over the past decade is the growth of e-commerce. This trend represented a fundamental shift in consumer behaviour and retail operations, driven by advancements in technology, changes in shopping habits, global reach and the increasing convenience of online transactions.
Investment opportunities
Position traders can capitalise on this primary trend by investing in various
segments of the e-commerce ecosystem:
- Online retailers - Companies like Amazon, Alibaba, and Shopify, which have established dominant positions in the e-commerce market.
- Payment processors - Firms such as PayPal that facilitate secure online transactions.
- Logistics and Delivery Services - Companies like FedEx and UPS that support the delivery infrastructure essential for e-commerce.
- Technology providers - Businesses that offer e-commerce solutions, including website development, cybersecurity, and digital marketing.
How do I manage risk in position trading?
By implementing the following risk management strategies, position traders can protect their capital, minimise losses, and enhance the potential for consistent, long-term returns. Here are key strategies to manage risk effectively:
Diversification
- Spread investments - Diversify a portfolio across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions to reduce the impact of a poor performance in any single investment.
- Avoid concentration - Avoid over-allocating to a single stock or sector, which increases exposure to specific risks.
Position sizing
- Limit investment per trade - Determine a maximum percentage of total capital to allocate to any single trade, typically ranging from 1-5%, depending on individual risk tolerance.
- Risk-to-reward ratio - Aim for trades with a favourable risk-to-reward ratio, ideally 1:2 or higher, meaning the potential reward is at least twice the potential risk.
Stop-Loss orders
- Set stop-loss levels - Use stop-loss orders to automatically sell a position if it reaches a predetermined price, limiting potential losses.
- Trailing stops - Consider trailing stops, which adjust the stop-loss level as the asset price moves in favour, booking profits while still limiting losses.
Regular review and adjustment
- Monitor portfolio - Regularly review the portfolio to ensure that investment positions align with risk tolerance and market conditions.
- Rebalance - Adjust the portfolio periodically to maintain desired asset allocation and risk profile, especially after significant market movements.
Fundamental and technical analysis
- Conduct thorough analysis - Base investment decisions on solid fundamental analysis, such as financial health, industry trends, and economic conditions. Use technical analysis to identify optimal entry and exit points.
- Stay informed - Keep up with market news, economic indicators, and company reports to anticipate changes that could impact positions.
Avoid over-leverage
- Limit use of margin - Using margin or leverage can amplify both gains and losses. Use leverage cautiously and be aware of the risks, including margin calls.
Psychological discipline
- Emotional control - Avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions. Stick to trading plans and risk management rules.
- Long-term perspective - Maintain a long-term investment outlook, which can help mitigate the impact of short-term market volatility.
What role do economic indicators and news play in position trading?
Economic indicators and news play a significant role in position trading, where traders hold positions for an extended period based on long-term market trends. These factors provide critical insights into the economic environment and can influence the valuation of assets and the direction of markets. Staying informed about economic indicators and news allows position traders to make sound decisions, aligning strategies with the broader economic environment and market trends. Here’s how they can impact position trading:
Economic indicators
- GDP - Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the overall economic output and growth of a country. Strong GDP growth often leads to bullish market sentiment, favouring long positions in equities and other growth-sensitive assets.
- Inflation - Inflation affects purchasing power and interest rates. High inflation can lead to tighter monetary policy, influencing interest rate-sensitive investments like bonds. Traders might adjust their portfolios based on expected changes in inflation.
- Interest Rates - Central banks set interest rates, which impact borrowing costs and economic activity. Lower rates generally support economic growth and asset prices, while higher rates can dampen growth and reduce asset valuations. Position traders often monitor central bank communications for clues about the direction of future rate changes.
- Employment Data - Employment reports, such as non-farm payrolls, indicate
- the health of the labour market and consumer spending potential. Strong employment numbers can signal economic strength, while weak data might suggest economic slowdown.
- Consumer Confidence and Spending - Indicators like consumer confidence and retail sales measure consumer sentiment and spending behaviour. Higher consumer confidence can lead to increased spending and economic growth, positively impacting stocks and other assets.
Websites like Pepperstone provide free comprehensive calendars with user-friendly charts to help analyse trends.
News events
- Corporate Earnings Reports - Quarterly earnings reports provide insights into a company's performance and future outlook. Positive earnings surprises can boost stock prices, while disappointing results can lead to declines.
- Geopolitical Events - Geopolitical developments, such as trade disputes, political instability, or conflicts, can significantly impact markets. Position traders need to consider these events, as they can cause market volatility and affect long-term trends.
- Regulatory Changes - Changes in regulations, such as tax policies, environmental laws, or trade tariffs, can have substantial effects on specific sectors or the broader market. Traders may need to adjust positions in response to such changes.
- Commodity Prices - News related to commodity prices, such as oil or precious metals, can influence related stocks and sectors. For example, rising oil prices might benefit energy companies but hurt sectors dependent on transportation.
- Technological and Industry Developments - Innovations and changes in industries can create new opportunities or disrupt existing markets. Staying informed about technological advancements helps position traders identify emerging trends and invest in future growth areas.
How position traders should consider using this information:
- Identify Long-Term Trends - By analysing economic data and news, traders can anticipate future market movements and align positions with prevailing trends.
- Adjust Portfolios - Significant economic shifts or news events may prompt traders to reallocate assets to manage risk or capitalise on new opportunities.
- Set Entry and Exit Points - Economic and news analysis helps determine the best times to enter or exit positions, optimising returns and managing downside risk.
How do I set realistic profit targets and stop-loss levels in position trading?
To set realistic profit targets and stop-loss levels in position trading consider the following:
Profit targets
- Technical Analysis - Use support/resistance levels, trendlines, and Fibonacci retracement levels.
- Fundamental Analysis - Consider valuation metrics and growth projections.
- Risk-to-Reward Ratio - Aim for a favourable ratio, typically 1:2 or higher.
Stop-Loss levels
- Technical Levels - Place stops below support levels or key moving averages.
- Percentage or Dollar-Based - Determine a fixed percentage or dollar amount you're willing to lose.
- Volatility Consideration - Adjust stops for the asset's volatility.
Regularly review and adjust based on market conditions, and maintain discipline in adhering to plans.
What is the best way to develop a position trading strategy?
Developing a successful position trading strategy involves a systematic approach that incorporates both technical and fundamental analysis, risk management, and ongoing evaluation. Here’s a structured approach to developing a position trading strategy:
Define trading goals and risk tolerance
- Set clear objectives - Determine ultimate goal such as capital appreciation, dividend income or a combination.
- Assess risk tolerance - Understand risk tolerance, which will ultimately influence asset selection and position sizing.
Choose market and instruments
- Select Asset Classes - Decide whether to trade foreign exchange, stocks, ETFs, commodities, or other instruments.
- Identify Sectors or Industries - Focus on areas with existing knowledge or see growth potential.
Conduct fundamental analysis
- Analyse Financial Health - Look at company financials, such as earnings, revenue growth, debt levels, and profitability.
- Evaluate Valuation Metrics - Use P/E ratios, P/B ratios, and other valuation tools to find undervalued or overvalued assets.
- Consider Macro Factors - Assess the broader economic environment, including interest rates, economic growth, and geopolitical factors.
Incorporate technical analysis
- Identify trends - Use tools like moving averages, trendlines, and chart patterns to determine the direction of the market or asset.
- Determine entry and exit points - Use indicators like support and resistance levels, RSI, and MACD to time your trades.
- Volume analysis - Consider trading volume to confirm trends and breakouts.
Set risk management rules
- Stop-Loss Orders - Define stop-loss levels to limit potential losses.
- Position Sizing - Allocate capital based on risk tolerance, ensuring no single trade can significantly impact the portfolio.
- Diversification - Spread investments across different assets or sectors to mitigate risk.
Develop a trading plan
- Document your strategy - Write down entry and exit criteria, risk management rules, and the rationale behind strategy.
- Backtesting - Test strategies using historical data to see how it would have performed in the past.
- Paper trading - Practice strategy in a simulated environment to gain confidence before committing real capital. Pepperstone’s Trading Simulator is a useful tool to consider for practicing the different strategies of swing trading.
Monitor and review
- Track performance - Regularly review trades and performance metrics to assess effectiveness of adopted strategy.
- Adjust and adapt - Be prepared to adjust the strategy in response to changing market conditions, new information, or lessons learned from past trades.
Continuous learning
- Stay informed - Keep up with market news, economic reports, and industry developments. Pepperstone provides comprehensive market coverage to help prepare for all major market moving events. Consider following Pepperstone’s senior analysts Chris Weston (@ChrisWeston_PS) and Michael Brown (@MrMBrown) on X (Twitter) for insight.
- Improve skills - Continuously learn about trading strategies, technical and fundamental analysis, and risk management techniques.
How do I evaluate the performance of my position trades?
Evaluating the performance of position trades is crucial to understanding trading effectiveness, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring any strategy aligns with financial goals. Here are key steps and metrics to evaluate position trading performance:
Track and record trades
- Maintain a trading journal - Detailed records of each trade, including entry and exit points, reasons for entering the trade, position size, stop-loss and take-profit levels, and the outcome should be kept. Keep a paper or free online trading journal such as TradeBench.
- Capture key metrics - Record metrics such as trade duration, realised gains or losses, and transaction costs.
Key performance metrics analysis
- Total return - Calculate the overall return of a portfolio over a specific period, including dividends and interest, relative to the initial investment.
- Average return per trade - Determine the average gain or loss per trade to understand typical trade performance.
- Win rate - Measure the percentage of trades that were profitable versus total trades. A higher win rate indicates a greater proportion of successful trades. Calculate the percentage of winning trades compared to the total number of trades. A higher win rate mostly indicates a more successful strategy, but it should be evaluated in conjunction with other metrics. If a trader manages risk well and limits losses on losing trades, even a 40% win rate can still lead to profitability.
Win Rate = Number of winning trades / (Number of winning traders + Number of losing traders) x 100%
- Risk-to-reward ratio - Assess the ratio of average profit to average loss on trades. A ratio greater than 1 indicates that your gains outweigh your losses. Most traders’ ideal risk-reward is 1:3 as it has a high return ratio but not very risky. The ratio means that there is $3 profit for every $1 committed to a trade. Normally the higher the risk/reward ratio the lower the win ratio and vice versa. The risk-reward should always be used in conjunction with the win rate.
Risk/Reward | Win Rate % Required |
| 1:10 | 9% |
| 1:5 | 17% |
| 1:4 | 20% |
| 1:3 | 25% |
| 1:2 | 33% |
| 1:1 | 50% |
| 1:0.5 | 67% |
| 1:0.3 | 75% |
- Drawdown - Evaluate the maximum drawdown, which is the largest peak-to-trough decline in a portfolio's value. This helps gauge risk and the potential for capital loss. Measure the largest peak-to-trough decline in the trading equity. A smaller maximum drawdown indicates better risk management and stability.
Maximum Drawdown = (Capital Peak High-Capital Trough Low)/ Capital Peak High
How can I stay updated on market conditions relevant to my position trades?
Staying updated on market conditions relevant to your position trades is crucial for making informed decisions and adjusting your strategy as needed. Here are several strategies and tools you can use to keep on top of market developments:
Financial news outlets
- News websites: Regularly check reputable financial news websites like Bloomberg, Reuters for updates on economic data, corporate earnings, and market trends.
Economic calendars
- Economic events: Use economic calendars to track important events such as central bank meetings, GDP releases, inflation reports, and employment data. Websites like Trading Economics or Pepperstone provide comprehensive calendars with user-friendly charts to help analyse trends.
- Earnings calendars: Follow earnings calendars to know when companies in your portfolio or sectors of interest are reporting their financial results.
Market analysis reports
- Brokerage Reports: Utilise reports from your brokerage, which often provide market analysis, sector updates, and stock recommendations.
Financial and trading apps
- Market Data Apps: Use apps like Bloomberg or Reuters for real-time market data, news, and alerts. Free aggregation platforms like #PiQ offer over 100 sources of information from the likes of Reuters and Bloomberg.
- Brokerage Apps: Many brokers offer mobile apps with integrated news feeds, research, and analysis tools.
Social Media
- X (Twitter): Follow reputable financial analysts, economists, and market commentators on Twitter for quick insights and market commentary.
Email newsletters and alerts
- Newsletters: Subscribe to newsletters from financial analysts, market commentators, or financial news websites to receive regular updates and insights.
- Custom Alerts:Set up custom alerts for specific stocks, sectors, or economic indicators using tools provided by financial websites or brokerage platforms.
Podcasts and webinars
- Podcasts: Listen to financial podcasts that cover market news, interviews with industry experts, and detailed analysis.
- Webinars and Seminars: Attend webinars hosted by financial experts or institutions for deeper insights into market conditions and trends.
Technical and fundamental analysis tools
- Charting Software: Use charting tools like TradingView, MetaTrader, or a broker’s platform to monitor technical indicators and price movements.
- Screeners and Scanners: Utilise stock screeners and scanners to identify potential trading opportunities and stay updated on market conditions.
Engage with financial advisors or mentors
- Consult Advisors: If at all possible, work with a financial advisor or mentor who can provide personalised insights and help stay informed about market conditions relevant to position trading.
Can I combine position trading with other trading styles?
Position trading can be combined and even enhanced with other trading styles. This approach is known as a hybrid trading strategy and can leverage the advantages of multiple trading techniques to optimise a portfolio's performance.
Position Trading and Swing Trading
- Time Frame Diversification - While position trading involves holding assets for months or years, swing trading focuses on shorter time frames, typically days to weeks. Combining these styles allows for the capture of long-term growth while also taking advantage of shorter-term market movements.
- Complementary Analysis - Use technical analysis for both styles, but adjust the indicators and chart periods. For position trades, focus on weekly or monthly charts, while for swing trades, use daily or intraday charts.
Position trading and day trading
- Core and Satellite Strategy - Maintain a core position trading portfolio for long-term growth and stability. Use a separate portion of capital for day trading, where trading can be undertaken actively within a single day to capitalise on intraday price movements.
- Risk Allocation - Allocate a smaller percentage of a portfolio to day trading, given its higher risk, while the majority remains in position trades.
Position trading and scalping
- Separate Capital and Accounts - Due to the vastly different nature and time commitment of scalping versus position trading, consider using separate accounts or clearly defined portions of capital for each style.
- Technology and Tools - Scalping often requires advanced trading tools and platforms with fast execution speeds, while position trading can rely on more traditional platforms and analysis methods.
Position trading and trend following
- Alignment of Strategies - Trend following aligns well with position trading since both styles benefit from capturing significant price trends over time. Use trend-following indicators like moving averages or trend lines to identify and hold onto long-term trends within position trades.
Position trading and value investing
- Fundamental Focus - Integrate value investing principles by selecting stocks for position trades based on fundamental analysis, targeting undervalued companies with strong growth potential.
- Patience and Long-Term Perspective - Both styles emphasise a long-term investment horizon, allowing a portfolio to be constructed of high-quality assets that can be held through market volatility.
Position trading and sector rotation
- Sector Allocation - Use sector rotation strategies to adjust a position trading portfolio based on macroeconomic cycles and sector performance. This involves shifting capital into sectors that are expected to outperform while reducing exposure to underperforming sectors.
- Diversification - This approach helps in diversifying a portfolio and potentially reducing risk by not being overly concentrated in one sector.
Position Trading FAQs
What are the best types of assets for position trading (e.g., stocks, forex, commodities)?
The best types of assets for position trading will depend on the individual:
- Stocks: Provide long-term growth potential.
- Forex: Offers liquidity and diverse market opportunities.
- Commodities: Hedge against inflation and diversify portfolios.
- Bonds: Provide stable returns and lower risk.
How do I determine the right entry and exit points for a position trade?
To determine entry and exit points for a position trade, combine fundamental analysis (evaluating company financials and growth prospects) with technical analysis (using support/resistance levels, trendlines, and indicators like moving averages). This dual approach helps identify undervalued stocks for entry and optimal moments to exit based on market trends.
How much capital is needed to start position trading?
Overall, the capital requirement depends on the asset class, trading frequency, and individual risk tolerance. Starting with a well-capitalised account helps manage trades effectively and withstand market volatility. Many industry experts recommend starting with at least $10,000-50,000 to ensure sufficient diversification and risk management. This range allows traders to absorb market fluctuations and avoid overexposure to a single asset. Forex trading can be started with as little as $1,000, though $10,000 is recommended for significant position trading to leverage better and manage risks. Trading commodities or bonds may require higher capital due to contract sizes and market volatility. Starting with at least $10,000-20,000 is prudent to effectively manage positions and potential margin requirements.
How do dividends and other corporate actions affect position trades?
Dividends and corporate actions, such as stock splits or mergers, impact position trades by altering stock value and potential returns. Dividends provide income and may influence stock price movements. Corporate actions can change share count or company structure, affecting valuation and strategic decisions for position traders.
The material provided here has not been prepared in accordance with legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research and as such is considered to be a marketing communication. Whilst it is not subject to any prohibition on dealing ahead of the dissemination of investment research we will not seek to take any advantage before providing it to our clients.
Pepperstone doesn’t represent that the material provided here is accurate, current or complete, and therefore shouldn’t be relied upon as such. The information, whether from a third party or not, isn’t to be considered as a recommendation; or an offer to buy or sell; or the solicitation of an offer to buy or sell any security, financial product or instrument; or to participate in any particular trading strategy. It does not take into account readers’ financial situation or investment objectives. We advise any readers of this content to seek their own advice. Without the approval of Pepperstone, reproduction or redistribution of this information isn’t permitted.